Semiconductor Types: Key Takeaways
- Semiconductors are the backbone of modern electronics, found in everything from smartphones and solar panels to electric vehicles and AI chips
- They are categorized into intrinsic (pure) and extrinsic (doped) types, with doping dramatically enhancing electrical conductivity
- P-type semiconductors use trivalent dopants and rely on “holes” (missing electrons) to conduct electricity
- N-type semiconductors use pentavalent dopants and conduct using free electrons
- Together, P-type and N-type materials form P-N junctions, the building blocks of critical components like diodes, LEDs, and transistors
More than 57% of the world’s semiconductors end up inside PCs, smartphones, and communication gear.
That includes the phone you’re holding, the laptop you’re working on, and even the systems keeping planes in the air. Some of these chips are pure; others are chemically tuned for speed and performance.
Here’s what we’ll walk through:
- What semiconductors are and how they work
- The difference between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors
- How P-type and N-type materials are formed
- Why doping changes conductivity
- Real-world applications of each semiconductor type
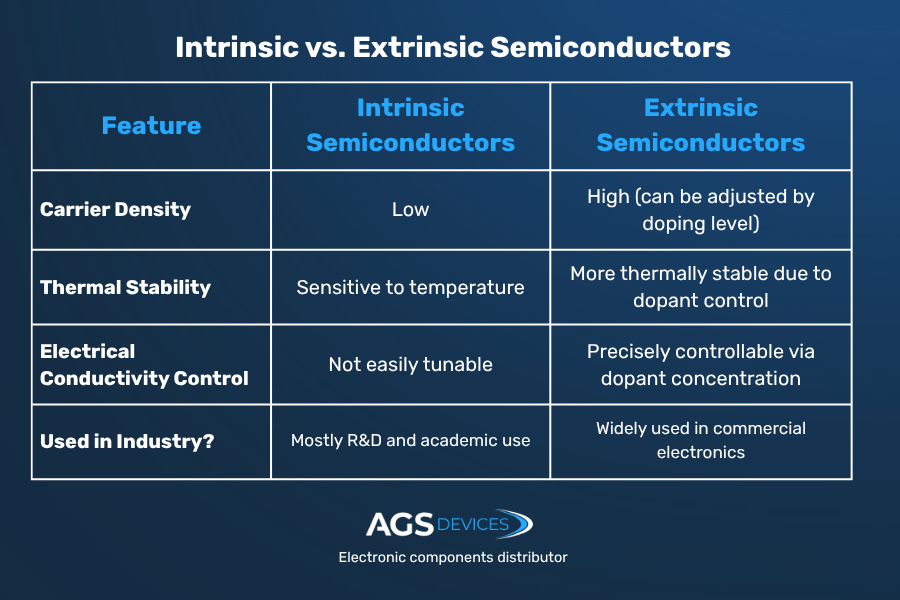
Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Semiconductors Explained
At the core of every electronic device lies a semiconductor, but not all semiconductors start the same way. They’re classified as either intrinsic or extrinsic, depending on whether they’re pure or modified.
Intrinsic Semiconductor
An intrinsic semiconductor is made of pure material, usually silicon or germanium, with no added impurities.
In its natural state:
- It has equal numbers of electrons and holes (empty states where electrons could go)
- Conductivity is relatively low and depends heavily on temperature
- It’s often used to study baseline behavior before doping
Example of an intrinsic semiconductor: pure silicon crystal.
Extrinsic Semiconductor
Extrinsic semiconductors are doped, which means that they are intentionally mixed with trace elements to improve their conductivity.
There are two main types:
- N-type: Doped with elements that add free electrons (e.g., phosphorus)
- P-type: Doped with elements that create holes (e.g., boron)
Doping transforms a weak conductor into a material that can be finely tuned for use in:
- Diodes
- Transistors
- Logic gates
- Solar cells
Because we can fine-tune how they move electricity, extrinsic semiconductors have become essential, powering everything from processors to power supplies.
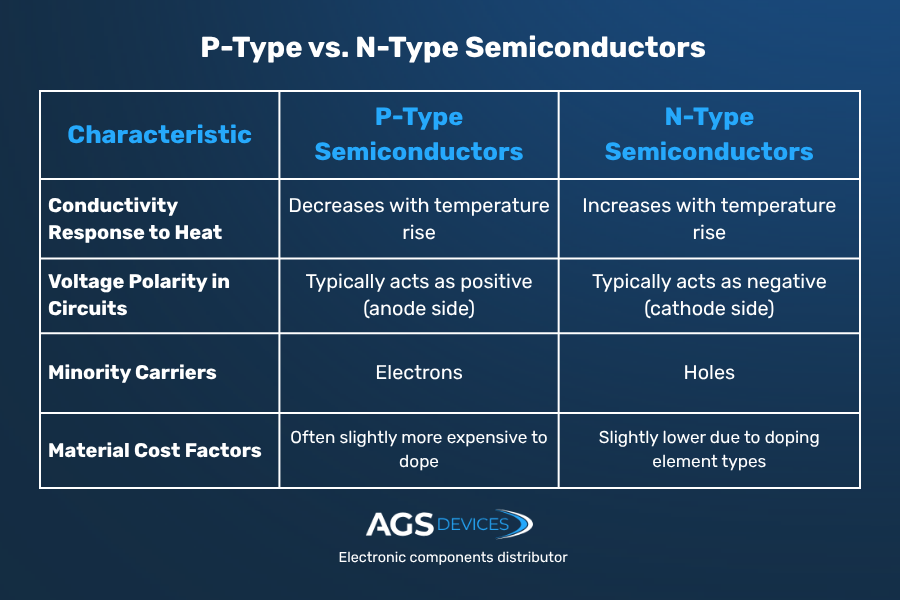
Key Differences Between P-Type and N-Type Semiconductors
Both P-type and N-type semiconductors are forms of extrinsic semiconductors, enhanced with specific impurities to control how they conduct electricity.
What Is a P-Type Semiconductor?
A P-type semiconductor is created by doping a pure semiconductor with a trivalent element (such as boron). This introduces holes or the absence of electrons, which act as the primary charge carriers.
- Majority carriers: Holes
- Doping element: Trivalent (e.g., boron, gallium)
- Charge movement: Positive (due to missing electrons)
- Function: Typically acts as the anode in a P-N junction
- Common uses: LEDs, solar cells, and base regions of transistors
You can think of it like a dance: electrons hop between atoms to fill in the blanks, and that movement creates electrical flow.
What Is an N-Type Semiconductor?
N-type semiconductors are doped with pentavalent elements (like phosphorus), which donate extra electrons to the crystal structure. These free electrons carry the current.
- Majority carriers: Electrons
- Doping element: Pentavalent (e.g., phosphorus, arsenic)
- Charge movement: Negative (due to surplus electrons)
- Function: Typically acts as the cathode in a P-N junction
- Common uses: Logic circuits, microchips, and emitters in transistors
N-type materials are prized for their high mobility and conductivity, making them essential in digital applications.
Applications of Different Semiconductor Types
Each type, from intrinsic to P-type and N-type, plays a distinct role depending on the design and function of the component.
Intrinsic Semiconductors
Primary use: Research and development
- Intrinsic semiconductors like pure silicon or germanium are often used in laboratories and academic settings to study baseline electrical behavior before doping
- Though they aren’t practical in most modern electronics, they provide the foundation for understanding semiconductor physics
Extrinsic Semiconductors: P-Type and N-Type
The real-world power of semiconductors comes from controlled doping, which creates P-type and N-type materials used in most devices today.
P-Type Applications
- P-N junction diodes: Act as the anode side
- Solar cells: Absorb light and creates electron-hole pairs
- LEDs: Emit light when recombination occurs
- Bipolar junction transistors (BJT): Used as the base region in amplification circuits
N-Type Applications
- Logic gates and microprocessors: Backbone of digital computing
- Field effect transistors (FETs): Widely used for switching and amplification
- Photodetectors: Convert light into electrical signals
- Cathode region in diodes: Complements P-type in rectification
P-N Junctions: Where It All Comes Together
When P-type and N-type semiconductors are joined, they form a P-N junction, the core of:
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in one direction
- Transistors: Amplify or switch electronic signals
- Solar panels: Convert sunlight into usable electric energy
Whether it’s crunching numbers or streaming your favorite show, these tiny materials are behind nearly every digital task we take for granted.
Why Source Semiconductors From AGS Devices
At AGS Devices, even in a semiconductor shortage, we help engineers, educators, and innovators make sense of semiconductor fundamentals and apply them to real-world electronic design and semiconductor manufacturing challenges.
Here’s how we make semiconductor sourcing simpler, smarter, and more secure:
- Global sourcing reach: Our supplier network spans North America, Europe, and Asia, giving you access to hard-to-find materials, including Si, GaAs, SiC, InP, and other doped semiconductors, even during allocation or obsolescence periods
- Shortage & lifecycle support: We monitor semiconductor availability in real time, offer last-time buy opportunities, and locate drop-in replacements to help you avoid redesigns and keep production on schedule
- Certified quality assurance: All sourced components undergo rigorous testing and inspection to meet ISO 9001, AS9120, and IDEA-STD-1010-B standards, ensuring traceability and zero-defect compliance
- BOM-level engagement: Whether you’re designing power modules, logic circuits, or optoelectronics, our sourcing team works with your engineers to optimize BOMs and overcome component challenges before they impact timelines
- Transparent updates: We provide real-time visibility into lead times, stock changes, alternate parts, and risk flags, giving you the data you need to act fast and stay ahead of disruption
Besides semiconductors, we also provide electronic components such as:
Types of Semiconductors: FAQs
What are the main types of semiconductors?
The two main types are intrinsic semiconductors (pure materials like silicon) and extrinsic semiconductors, which are doped to enhance conductivity. Extrinsic semiconductors are further divided into P-type and N-type.
What is the difference between P-type and N-type semiconductors?
P-type semiconductors use trivalent dopants and conduct via holes (positive charge carriers), while N-type semiconductors use pentavalent dopants and conduct via free electrons (negative charge carriers).
What is an example of a semiconductor material?
Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor material, but others include germanium, gallium arsenide (GaAs), and silicon carbide (SiC), each with unique electrical and thermal properties.
Why are semiconductors important in electronics?
Semiconductors are essential because they allow controlled conductivity, making them perfect for building transistors, diodes, solar cells, and integrated circuits, the core components of modern electronics.
What is a P-N junction, and why is it important?
A P-N junction forms when P-type and N-type materials are joined. It creates an electric field that allows current to flow in one direction, enabling devices like diodes and LEDs to function efficiently.
