Did you know that the global electronic components market is projected to reach $643 billion by 2027, which is mainly driven by advancements in automotive, telecommunications, and industrial automation?
To keep this industry moving forward, precise component identification for engineers and technicians is one of the key steps to ensuring quality.
Today, we’re going to cover why identifying these components is important, provide you with techniques of identifying electronic components and give you additional expert tips you should know about.
Why Identifying Electronic Components Is Essential
In electronics, precise identification of components is critical for engineers, technicians, and manufacturers.
This process is important because it:
- Avoids costly design errors: Misidentifying components can lead to incorrect placements, failed circuits, or damage to the system.
- Ensures compatibility: Many components appear similar but have different voltage ratings, tolerances, or pin configurations that must match the circuit design.
- Reduces repair and maintenance time: Proper identification speeds up troubleshooting and component replacement, minimizing downtime.
- Prevents counterfeit risks: The electronic components market contains counterfeit parts. Knowing how to verify markings and specifications ensures reliability.
- Improves procurement accuracy: Engineers and purchasing teams need to match exact specifications when ordering parts for BOM management and supply chain logistics.

Understanding Circuit Board Components and Their Markings
Whether you’re working with resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, or integrated circuits (ICs), each part is labeled with a unique identifier.
How To Read Component Labels and Codes
Electronic components are often labeled with alphanumeric codes that show their value, tolerance, and other characteristics.
Here’s how each electronic component is labeled:
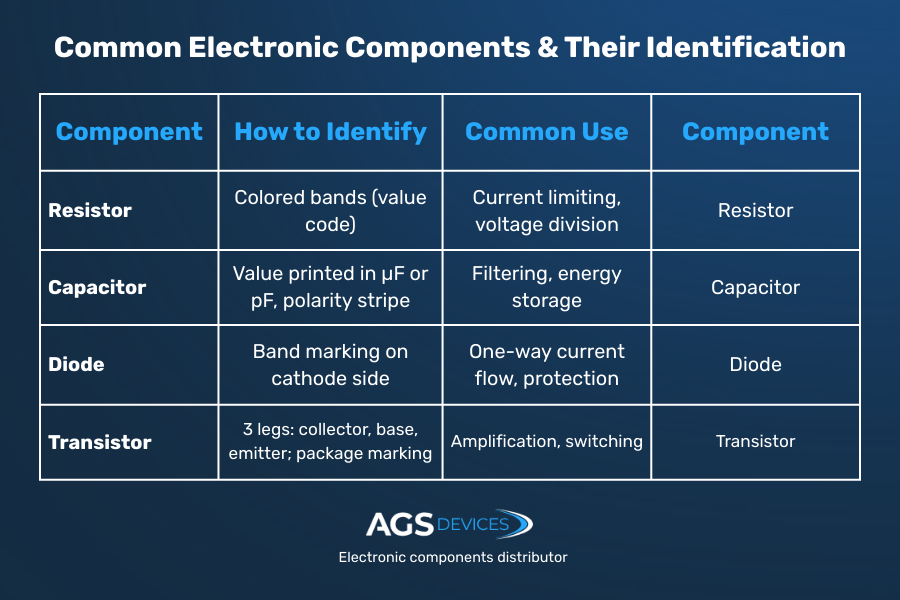
- Resistors: This component typically uses a three or four-band color code to indicate resistance value and tolerance.
- Capacitors: Ceramic capacitors are labeled with a three-digit code, where the first two digits indicate the capacitance value, and the third represents the multiplier. Electrolytic capacitors display capacitance (µF) and voltage rating directly.
- Diodes and Transistors: Often marked with a part number (e.g., 1N4007 for a rectifier diode or BC547 for an NPN transistor).
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): ICs have a manufacturer code, part number, and date code to indicate model specifications and production batch.
Identifying Common Circuit Board Components
Circuit boards have a mix of passive and active components, and each of those components has a role in signal processing, power management, and data transmission.
These components include:
- Resistors: Control current flow and are identified by color bands or numerical values.
- Capacitors: Store and release energy, labeled with capacitance and voltage ratings.
- Inductors: Used for energy storage and filtering, typically marked with inductance values (µH or mH).
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in one direction, labeled with a polarity indicator (cathode band) and part number.
- Transistors: Act as switches or amplifiers, featuring three leads labeled as base (B), collector (C), and emitter (E).
- ICs (Integrated Circuits): Packaged in dual in-line (DIP), surface-mount (SMD), or ball grid array (BGA) formats, with part numbers printed on the chip.
Deciphering Manufacturer Markings and Part Numbers
Each electronic component is marked with a part number that corresponds to a manufacturer-specific datasheet.
These markings indicate:
- Manufacturer name or logo: Found on ICs, transistors, and specialty components.
- Lot & date codes: Identify the production batch and manufacturing date.
- Country of origin: Some components include country-specific markings that indicate production location.
- Quality & compliance certifications: High-reliability components may display ISO, RoHS, or UL compliance marks.
Techniques for Identifying Electronic Components
Whether troubleshooting a circuit, verifying a component’s specifications, or checking for authenticity, the right approach ensures efficient diagnosis and prevents costly errors.
The most common techniques for identifying electronic components include:
1. Using Multimeters and Other Testing Equipment
Multimeters and specialized testing devices help measure electrical properties and confirm a component’s functionality.
Here’s what equipment you’re going to need:
- Multimeters: Measure resistance, capacitance, voltage, and continuity, making them essential for verifying resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors.
- LCR meters: Specifically used to test inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) for passive components.
- Semiconductor testers: Check transistor gain (hFE), diode polarity, and MOSFET behavior to determine if a component is functional.
- Oscilloscopes & signal analyzers: Used in advanced diagnostics to analyze waveforms and signal integrity in ICs and high-frequency components.
Testing components before installation ensures they meet circuit requirements and industry standards.
2. Online Databases and Component Reference Guides
Many electronic components have manufacturer-specific part numbers that can be cross-referenced using online databases and datasheets.
Resources you can use:
- Manufacturer websites: Leading semiconductor companies provide detailed datasheets that list component characteristics, pin configurations, and applications.
- Industry databases: Platforms like Mouser, Digi-Key, and Octopart allow users to search for electronic component specifications and availability.
- Component lookup tools: Search engines dedicated to part identification can match markings, lot numbers, and quality certifications to a specific part.
- Datasheets & PDFs: Engineers rely on downloadable technical documents to confirm voltage ratings, temperature tolerances, and application notes.
3. Visual Inspection Methods for Circuit Boards
A detailed visual inspection can reveal certain clues about a component’s function, condition, and authenticity.
You can look at:
- Silkscreen labels & PCB markings: Circuit boards often have printed identifiers (R for resistors, C for capacitors, U for ICs, etc.) that help with quick identification.
- Polarity & pin layouts: Components like diodes, electrolytic capacitors, and transistors have distinct markings (bands, dots, or cutouts) indicating proper orientation.
- Manufacturer logos & part numbers: ICs, transistors, and diodes typically have engraved or printed alphanumeric codes that match datasheets.
- Counterfeit detection: Authentic components should have consistent markings, smooth surfaces, and sharp printing. Blurred labels, irregular fonts, or missing logos may indicate counterfeit parts.
Identifying Specialty and Obsolete Components
Finding and verifying these components requires expertise, whether they’re rare, discontinued, or made with precious metals.
Here’s what the process typically looks like.
Identifying Hard-to-Find Electronic Components
Some components are no longer in production or have limited availability. Engineers often rely on manufacturer markings, cross-referencing part numbers, and trusted suppliers to locate these parts.
Legacy systems and military-grade electronics may use outdated numbering, requiring careful specification matching and industry database searches.
Locating Precious Metals in Electronics
Palladium, gold, and platinum are commonly found in multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), high-frequency connectors, and circuit board coatings.
These metals enhance conductivity and durability, especially in aerospace, telecom, and medical devices.
Engineers and recyclers focus on older, high-reliability components to recover valuable materials
Managing Discontinued Parts for Repairs
Industries like aviation, defense, and industrial automation rely on components designed decades ago.
When replacements are unavailable, engineers match old datasheets, check pin configurations, or find modern equivalents.
Custom fabrication or salvaging from donor boards can help restore aging systems, extending their lifespan.
Why Engineers and Technicians Trust AGS Devices for Component Sourcing
At AGS Devices, we provide the highest quality sourcing and use an innovative approach to ensure you avoid supply chain disruptions.
With strict quality control measures, a vast inventory, and expert procurement support, our company is a trusted partner for industries requiring precision, reliability, and compliance with global standards.
What notably sets us apart, includes:
- Verified & high-quality components: Every component undergoes rigorous testing and verification to prevent counterfeit risks and ensure performance.
- Sourcing hard-to-find & legacy parts: Whether you need discontinued semiconductors, rare inductors, or obsolete ICs, AGS leverages a global network of suppliers to find the right part.
- Industry-certified quality assurance: We adhere to ISO 9001:2015, AS9120B, and IDEA-STD-1010-B standards, ensuring components meet the highest reliability requirements.
- Efficient BOM management & procurement support: Our team works closely with engineers and procurement specialists to optimize sourcing strategies, prevent shortages, and reduce lead times.
- Reliable & on-time delivery: AGS ensures seamless logistics and timely fulfillment, supporting critical industries like aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and industrial automation.
With on-time delivery, expert sourcing support, and strict quality assurance, AGS Devices is the trusted partner for engineers and manufacturers worldwide.